
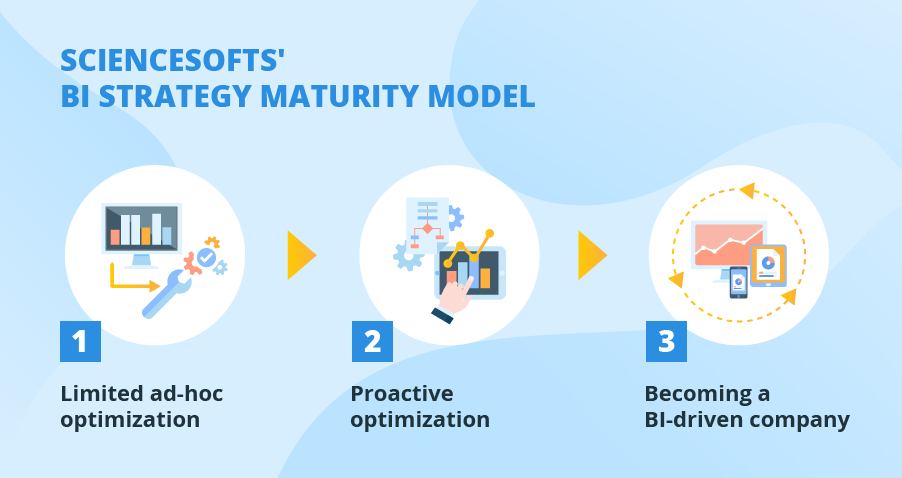
BI dashboards make it easy to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress against targets, and set alerts to know where and when to focus improvement initiatives. They can also assess their own capabilities, strengths, and weaknesses compared to competitors and use that information to their advantage. With timely BI, organizations can quickly identify and act on new trends and opportunities. Gain and maintain competitive advantage.BI tools help executives, managers, and workers uncover insights that are relevant to their roles and areas of responsibility – and use them to make decisions based on fact, not guesswork. Receive support for fact-based decision-making.Here are just a few of the many benefits of BI: Key benefits of business intelligenceĪ successful BI program shines light on ways to increase profits and performance, discover issues, optimize operations, and much more.
#Business intelligence strategy definition software#
This is why several major software vendors have started to combine BI and business analytics on a single cloud platform, providing organizations with all the analytics capabilities they need in one place – and rendering the whole taxonomy debate moot. Regardless of the label applied, what is important is that organizations have the tools and technology they need to get answers to their business questions, solve the problem at hand, or reach a specific goal.

“What’s the difference between business analytics and business intelligence? The correct answer is: everybody has an opinion, but nobody knows, and you shouldn’t care.” Timo Elliot, Innovation Evangelist, SAP

It answers questions like “What happened?” and “What needs to change?” – but it does not get into why something happened or what might happen next. Also known as a decision support system (DSS), a BI system analyzes current and historical data and presents findings in easy-to-digest reports, dashboards, graphs, charts, and maps that can be shared across the company.īI is sometimes called “descriptive analytics” because it describes how a business is performing today and how it performed in the past. Business intelligence definitionīusiness intelligence refers to the processes and tools used to analyze business data, turn it into actionable insights, and help everyone in an organization make better-informed decisions. To actually take advantage of this data, and use it to make data-driven decisions, they need a modern business intelligence (BI) system. Most companies collect a massive volume of business data every day – flowing in from their enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, e-commerce platform, supply chain, and many other internal and external sources. Governance, Risk, Compliance (GRC), and CybersecurityĮngineering, Construction, and Operations
Accounts Receivable, Billing and Revenue Management


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
